INCT GmbH
Blog Details
Planetary Gear Series — Chapter 1
2025-12-09
What Are Planetary Gears Used For? (Fundamentals & Applications)
A Complete Beginner-Friendly Guide for Engineers & Product Designers
Executive Summary / Why This Chapter Matters
Planetary gear systems are one of the most compact, efficient, and high-torque transmission mechanisms used in modern engineering. They appear in robots, CNC machines, EV transmissions, medical devices, wind turbines, and more.
This chapter gives you a clear understanding of:
1. What planetary gears are and how they work
2. Why engineers choose planetary gearboxes
3. When you should NOT use a planetary gearbox
4. The applications where planetary systems deliver the greatest value
If you are evaluating, selecting, or learning planetary gear systems, you are in the right place.
If you are already considering gearbox selection for a real project, you can directly continue to Chapter 3: How to Select a Planetary Gearbox, which focuses on torque calculation, reduction ratio, and practical constraints.
1. What Are Planetary Gears? — A Solar-System-Inspired Gear Mechanism
A planetary gearbox consists of four core components arranged like a miniature solar system:
• Sun Gear — center gear
• Planet Gears — 3–5 gears that orbit the sun
• Ring Gear (Internal gear) — outer gear with internal teeth
• Planet Carrier(1) — holds planet gears and usually acts as the output
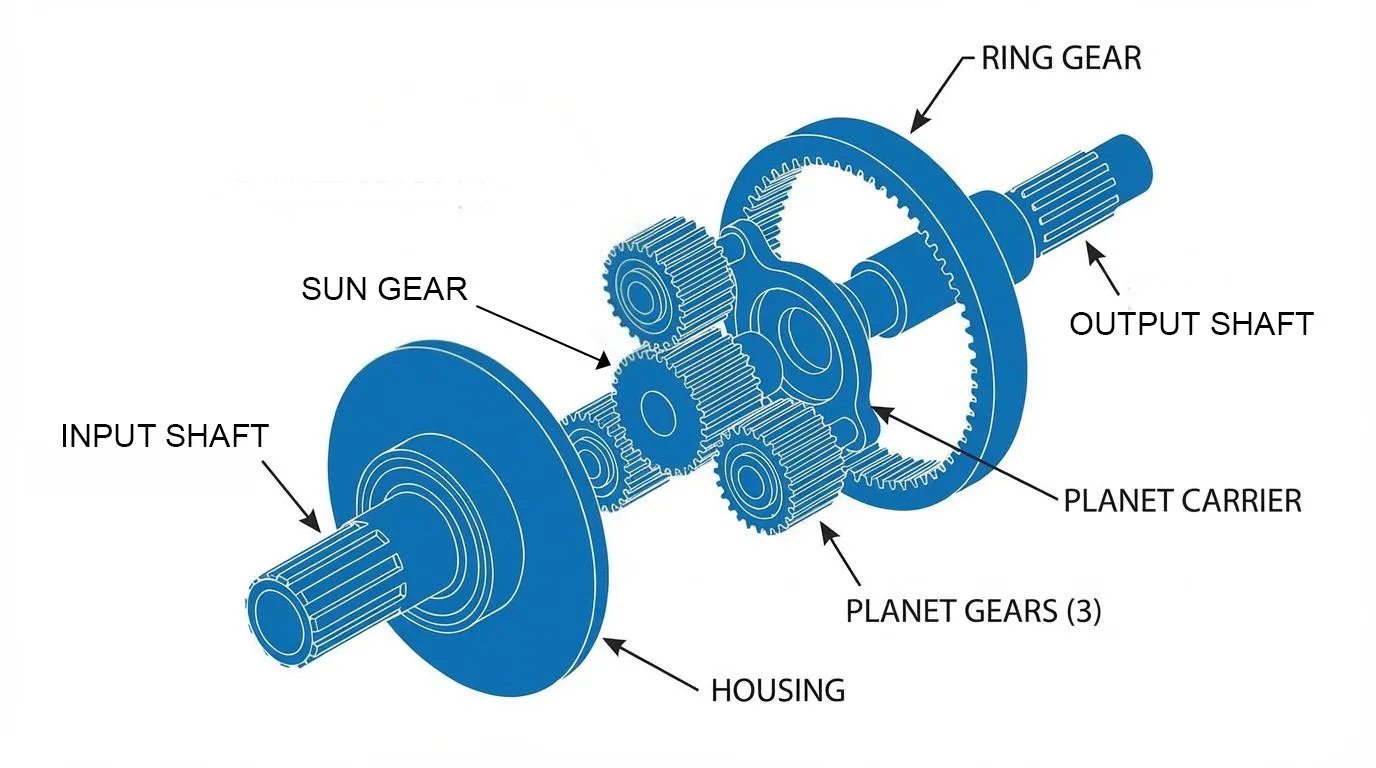
This unique multi-gear engagement allows the system to transmit very high torque in a compact body. The mechanical logic behind this torque multiplication and load sharing is explained in detail in Chapter 2: How Planetary Gear Systems Work, starting from torque transmission inside the gear set.
2. How the Structure Enhances Performance?
Planetary gearboxes outperform traditional spur or helical gear reducers because:
✔ Multi-point load sharing
3–5 planet gears share load simultaneously →
• Higher torque capacity
• Better load distribution
• Longer service life
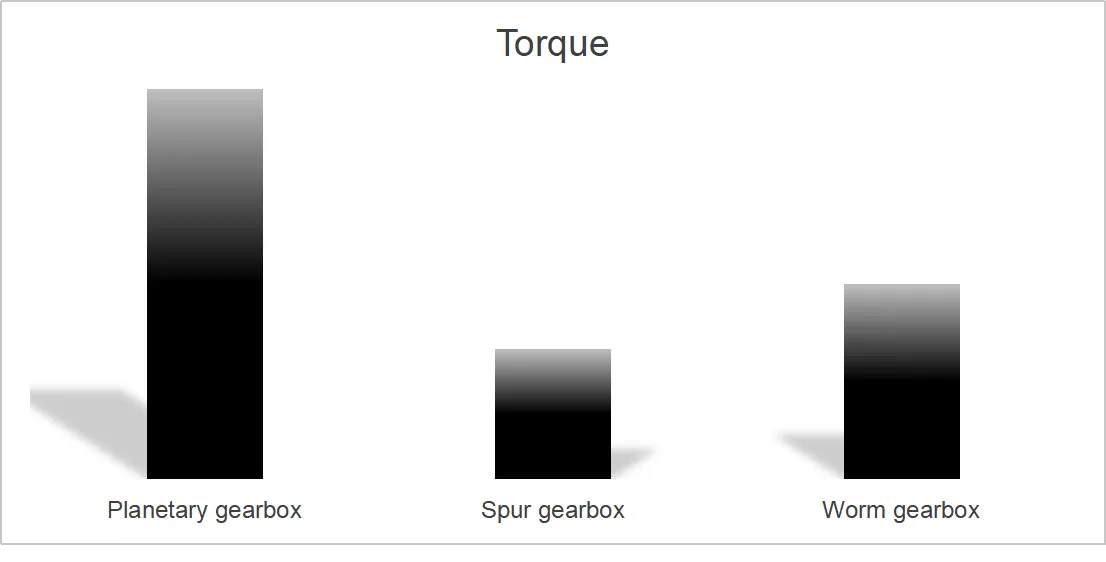
✔ High torque density(2)
Planetary gearboxes deliver 2–4× more torque than spur reducers of the same size.
✔ High mechanical efficiency
Typical precision planetary gearboxes achieve 95–98% efficiency under rated load with proper lubrication.
✔ High reduction ratios(3) in small size
Multiple stages can be stacked to achieve higher ratios while keeping the footprint compact.
✔ Low backlash(4)
Precision models reach ≤3 arc-min; premium models can reach ≤1 arc-min, essential for robotics, AGVs, CNC machines.
3. Key Advantages of Planetary Gear Systems
✅ High Torque Density — multiple gears share the load
✅ Low Backlash — ideal for servo positioning and robotics
✅ Smooth & Quiet Operation — symmetrical structure minimizes vibration
✅ High Rigidity & Durability — supports dynamic loads, shock loads
✅ Coaxial Input/Output — simplifies machine layout
✅ Wide Motor Compatibility — servo, BLDC, stepper, AC motors
4. Major Application Scenarios — Where Planetary Gears Perform Best
Planetary gear systems are chosen when high torque, high precision, and compact size are required.
4.1 Industrial Automation
Used in:
🎯 CNC machines
🎯 Packaging equipment
🎯 Conveyor systems
🎯 Industrial robots
Why: high precision, fast response, long lifetime.
4.2 Robotics (AGV/AMR, cobots, robotic joints)
Needs:
🎯 Low backlash
🎯 High rigidity
🎯 Compact structure
Planetary gearboxes are a standard solution for robot joints and AMR drives.
4.3 Automotive & EV Systems
Found in:
🎯 Automatic transmissions & EV drivetrains
🎯 Hybrid power split devices
🎯 Differential systems
Why: smooth shifting + efficiency + compactness.
4.4 Renewable Energy
Wind turbine uses:
🎯 Yaw drives
🎯 Pitch control
Why: ability to handle shock loads & fluctuating forces.
4.5 Power Tools & Medical Devices
Used in:
🎯 Surgical robots
🎯 Gimbal actuators
🎯 High-torque tools
Why: high power output in limited installation space.
5. Suitability Boundaries — When NOT to Use Planetary Gearboxes
Planetary gears are excellent, but not always the best choice.
|
Scenario |
Why Not |
Better Alternative |
|
Extreme low-budget projects |
Planetary gearboxes cost more than basic spur/worm types |
Spur or worm gear |
|
Single-stage ratios >100:1 |
Requires multi-stage planetary → cost & size increase |
|
|
Need for self-locking |
Planetary gearboxes cannot self-lock |
Worm gearbox |
|
Continuous unbalanced load |
May cause planet gear uneven wear |
Parallel-shaft gear reducer |
This helps readers avoid over-engineering or overpaying.
6. Summary — Why Planetary Gears Matter
Planetary gear systems provide:
💪 High torque output
💪 High efficiency
💪 Compact structure
💪 Low backlash
💪 Excellent durability
This makes them ideal for automation, robotics, EV systems, renewable energy, and precision machinery.
Glossary:
(1) Planet Carrier: Component that holds the planet gears.
(2) Torque Density: Torque produced per unit weight/volume.
(3) Reduction Ratio: How many times input speed is reduced.
(4) Backlash: The small rotational play between gear teeth.
This article is part of a complete 5‑chapter Planetary Gearbox Series.
Each chapter addresses a different engineering decision level, from fundamentals to real system integration.
👉 Chapter 2: How Planetary Gear Systems Work — A Deep Technical Breakdown
(Understand torque flow, load sharing, efficiency, and precision at a mechanical level)
👉 Chapter 3: How to Select a Planetary Gearbox — Torque, Ratios & Duty Cycle
(Practical selection guide for engineers and designers)
👉 Chapter 4: Planetary Gearbox vs Other Gear Systems — Technical Comparison
(Compare planetary, spur, worm, cycloidal, and harmonic solutions)
👉 Chapter 5: How Planetary Gearboxes Are Used in Real Industrial Systems
(System-level integration logic in robotics, automation, and EV applications)
What Are Planetary Gears Used For? (Fundamentals & Applications)
A Complete Beginner-Friendly Guide for Engineers & Product Designers
Executive Summary / Why This Chapter Matters
Planetary gear systems are one of the most compact, efficient, and high-torque transmission mechanisms used in modern engineering. They appear in robots, CNC machines, EV transmissions, medical devices, wind turbines, and more.
This chapter gives you a clear understanding of:
1. What planetary gears are and how they work
2. Why engineers choose planetary gearboxes
3. When you should NOT use a planetary gearbox
4. The applications where planetary systems deliver the greatest value
If you are evaluating, selecting, or learning planetary gear systems, you are in the right place.
If you are already considering gearbox selection for a real project, you can directly continue to Chapter 3: How to Select a Planetary Gearbox, which focuses on torque calculation, reduction ratio, and practical constraints.
1. What Are Planetary Gears? — A Solar-System-Inspired Gear Mechanism
A planetary gearbox consists of four core components arranged like a miniature solar system:
• Sun Gear — center gear
• Planet Gears — 3–5 gears that orbit the sun
• Ring Gear (Internal gear) — outer gear with internal teeth
• Planet Carrier(1) — holds planet gears and usually acts as the output

This unique multi-gear engagement allows the system to transmit very high torque in a compact body. The mechanical logic behind this torque multiplication and load sharing is explained in detail in Chapter 2: How Planetary Gear Systems Work, starting from torque transmission inside the gear set.
2. How the Structure Enhances Performance?
Planetary gearboxes outperform traditional spur or helical gear reducers because:
✔ Multi-point load sharing
3–5 planet gears share load simultaneously →
• Higher torque capacity
• Better load distribution
• Longer service life
✔ High torque density(2)
Planetary gearboxes deliver 2–4× more torque than spur reducers of the same size.
✔ High mechanical efficiency
Typical precision planetary gearboxes achieve 95–98% efficiency under rated load with proper lubrication.
✔ High reduction ratios(3) in small size
Multiple stages can be stacked to achieve higher ratios while keeping the footprint compact.
✔ Low backlash(4)
Precision models reach ≤3 arc-min; premium models can reach ≤1 arc-min, essential for robotics, AGVs, CNC machines.

3. Key Advantages of Planetary Gear Systems
✅ High Torque Density — multiple gears share the load
✅ Low Backlash — ideal for servo positioning and robotics
✅ Smooth & Quiet Operation — symmetrical structure minimizes vibration
✅ High Rigidity & Durability — supports dynamic loads, shock loads
✅ Coaxial Input/Output — simplifies machine layout
✅ Wide Motor Compatibility — servo, BLDC, stepper, AC motors
4. Major Application Scenarios — Where Planetary Gears Perform Best
Planetary gear systems are chosen when high torque, high precision, and compact size are required.
4.1 Industrial Automation
Used in:
🎯 CNC machines
🎯 Packaging equipment
🎯 Conveyor systems
🎯 Industrial robots
Why: high precision, fast response, long lifetime.
4.2 Robotics (AGV/AMR, cobots, robotic joints)
Needs:
🎯 Low backlash
🎯 High rigidity
🎯 Compact structure
Planetary gearboxes are a standard solution for robot joints and AMR drives.
4.3 Automotive & EV Systems
Found in:
🎯 Automatic transmissions & EV drivetrains
🎯 Hybrid power split devices
🎯 Differential systems
Why: smooth shifting + efficiency + compactness.
4.4 Renewable Energy
Wind turbine uses:
🎯 Yaw drives
🎯 Pitch control
Why: ability to handle shock loads & fluctuating forces.
4.5 Power Tools & Medical Devices
Used in:
🎯 Surgical robots
🎯 Gimbal actuators
🎯 High-torque tools
Why: high power output in limited installation space.
5. Suitability Boundaries — When NOT to Use Planetary Gearboxes
Planetary gears are excellent, but not always the best choice.
|
Scenario |
Why Not |
Better Alternative |
|
Extreme low-budget projects |
Planetary gearboxes cost more than basic spur/worm types |
Spur or worm gear |
|
Single-stage ratios >100:1 |
Requires multi-stage planetary → cost & size increase |
|
|
Need for self-locking |
Planetary gearboxes cannot self-lock |
Worm gearbox |
|
Continuous unbalanced load |
May cause planet gear uneven wear |
Parallel-shaft gear reducer |
This helps readers avoid over-engineering or overpaying.
6. Summary — Why Planetary Gears Matter
Planetary gear systems provide:
💪 High torque output
💪 High efficiency
💪 Compact structure
💪 Low backlash
💪 Excellent durability
This makes them ideal for automation, robotics, EV systems, renewable energy, and precision machinery.
Glossary:
(1) Planet Carrier: Component that holds the planet gears.
(2) Torque Density: Torque produced per unit weight/volume.
(3) Reduction Ratio: How many times input speed is reduced.
(4) Backlash: The small rotational play between gear teeth.
This article is part of a complete 5‑chapter Planetary Gearbox Series.
Each chapter addresses a different engineering decision level, from fundamentals to real system integration.
👉 Chapter 2: How Planetary Gear Systems Work — A Deep Technical Breakdown
(Understand torque flow, load sharing, efficiency, and precision at a mechanical level)
👉 Chapter 3: How to Select a Planetary Gearbox — Torque, Ratios & Duty Cycle
(Practical selection guide for engineers and designers)
👉 Chapter 4: Planetary Gearbox vs Other Gear Systems — Technical Comparison
(Compare planetary, spur, worm, cycloidal, and harmonic solutions)
👉 Chapter 5: How Planetary Gearboxes Are Used in Real Industrial Systems
(System-level integration logic in robotics, automation, and EV applications)